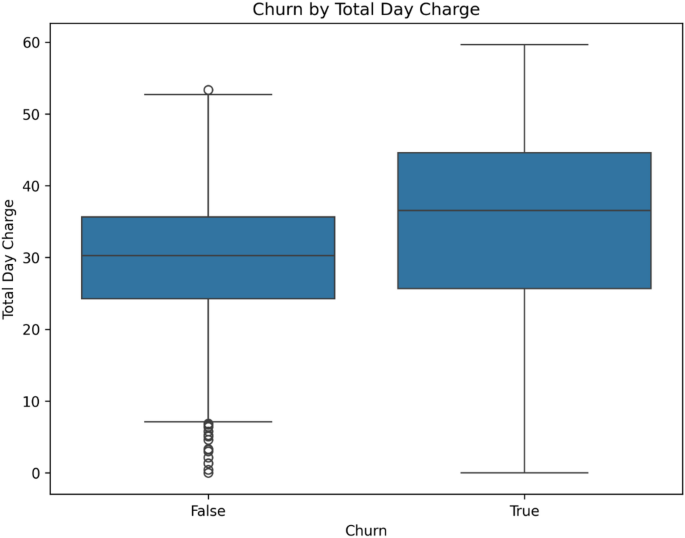
The empirical results of this study demonstrate not only the predictive power of the Random Forest model but also pave the way for its operationalization within customer relationship management systems. The high accuracy (0.9513) and strong discriminatory power (AUC = 0.89) provide a reliable foundation for proactive churn management. However, the model’s performance characteristics—specifically, its high precision (0.98) but moderate recall (0.68) for the churn class—suggest a strategic calibration that prioritizes the cost-efficient targeting of high-risk customers, even at the expense of missing some true churners. This trade-off is often acceptable in business contexts where retention campaign resources are finite.
From predictive insights to an integrated AI-CRM framework
The feature importance analysis, which identified service usage patterns (e.g., total day minutes, total day charge) and customer service interactions as primary churn drivers, allows for the translation of model outputs into a strategic framework. This framework moves beyond mere prediction to propose a suite of AI-augmented CRM capabilities, conceptually outlined below:
-
Proactive Retention Management: Instead of a “Smart Offers” algorithm, the model enables a data-driven retention strategy. Customers flagged as high-risk based on key features (e.g., high daily charge and multiple service calls) can be automatically routed into targeted intervention workflows within the CRM. Interventions can be personalized based on the specific drivers identified for each customer, such as offering tailored plan adjustments or proactive service credits.
-
Customer Micro-Segmentation: The application of clustering algorithms (e.g., K-Means) on the feature set, validated by the predictive model’s findings, can reveal distinct customer cohorts. Segments such as “High-Value International Users” or “Service-Needing Customers” allow for hyper-targeted marketing and service strategies, moving beyond demographic segmentation to behaviorally-driven micro-segments.
-
Dynamic Customer Value Optimization: By integrating churn probability with usage data, a dynamic view of Customer Lifetime Value (CLV) can be calculated. This enables value-based strategies, such as offering personalized pricing or loyalty incentives to high-value, at-risk customers, thereby maximizing revenue and retention simultaneously.
-
Cross-Channel Engagement Optimization: Analysis of customer interaction data can inform an optimal communication strategy. The model’s insights can guide the timing and channel for retention efforts—for instance, prioritizing direct channels like SMS or in-app notifications for high-urgency churn risks, while using email for broader educational campaigns.
Conceptual workflow for system integration
For full operationalization, the predictive model must be integrated into the corporate CRM ecosystem. A proposed conceptual workflow is as follows:
-
1.
Data Ingestion: Real-time customer data (usage, service tickets, billing) is fed into a pre-processing pipeline.
-
2.
Model Scoring: The deployed Random Forest model generates a churn probability and a reason code (based on feature importance) for each customer.
-
3.
CRM Trigger: Customers exceeding a pre-defined churn risk threshold are flagged within the CRM dashboard.
-
4.
Automated Action: Pre-defined rules trigger specific actions, such as assigning the customer to a dedicated retention agent, sending a personalized offer, or creating a service task to address a recurring issue.
Limitations and research implications
While this framework is promising, its development highlights several avenues for future research. The current study is limited by its reliance on a structured, historical dataset. Future work should investigate the integration of unstructured data sources, such as call center transcripts and social media sentiment, to enrich the feature set. Furthermore, the proposed operational framework requires longitudinal A/B testing in a live environment to quantitatively validate its impact on churn reduction and customer lifetime value. Finally, exploring more complex models, including deep learning and explainable AI (XAI) techniques, could further enhance both predictive accuracy and the interpretability of the drivers behind churn, fostering greater trust in the AI-driven recommendations.
In conclusion, this research provides a validated, end-to-end pathway from AI-powered churn prediction to actionable CRM strategy. The proposed integrated framework demonstrates how data-driven insights can transform customer relationship management from a reactive function to a proactive, value-centric operation within the telecommunications industry.
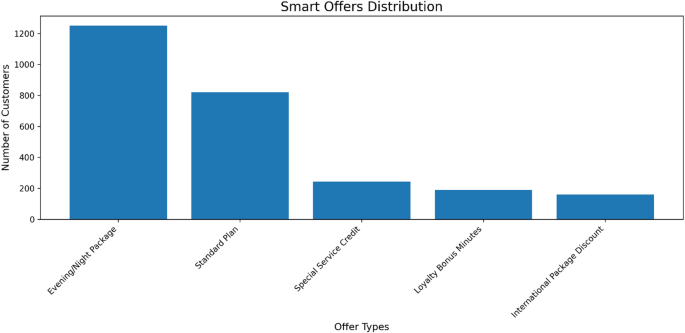
Adoption rates of different proactive retention offers deployed to at-risk customers. The distribution highlights a stronger customer preference for service-enhancement packages (e.g., Evening/Night Package) compared to direct credits or discounts, informing the prioritization of retention strategies.
The translation of churn risk into proactive retention strategies can be informed by customer engagement data. An analysis of offer adoption rates (Fig. 11) reveals a clear preference for service-based packages, such as the ‘Evening/Night Package,’ over direct monetary incentives like ‘Special Service Credit.’ This suggests that retention efforts are more effective when they enhance service value and align with customer usage patterns, rather than simply providing financial compensation. These findings underscore the importance of leveraging actionable intelligence from the CRM to personalize interventions, ensuring that retention resources are allocated to the most resonant offers for different customer segments.
Frequency of AI-generated service recommendations. Usage-centric packages (Night Unlimited, International Roaming) were recommended most frequently, indicating key areas for service portfolio development and targeted customer engagement.
The analysis of service recommendation uptake provides further evidence for data-driven cross-selling strategies within a CRM. As shown in Fig. 12, recommendations for usage-based packages, specifically the ‘Night Unlimited Package’ and ‘International Roaming Package’, were generated significantly more often than others. This pattern indicates that customer needs are heavily oriented towards flexibility and expanded service capabilities. The low incidence of ‘No additional services needed’ suggests a receptive customer base for targeted upselling. These findings validate that AI-driven recommendations, when aligned with prevalent customer usage patterns, can effectively guide the development of personalized service offerings to enhance retention and value.
Distribution of recommended price tiers generated by the AI-driven pricing engine. The predominance of the Standard Tier reflects its alignment with the value proposition for the majority of the customer base, while the Economy and Premium tiers enable targeted segmentation.
The output of the dynamic pricing logic reveals a strategic segmentation of the customer base, as visualized in Fig. 13. The majority of customers (71.8%) were recommended the ‘Standard Tier,’ indicating that this option represents the optimal balance of value and features for the core customer segment. The smaller but distinct allocations to ‘Economy’ (16.1%) and ‘Premium’ (12.1%) tiers demonstrate the model’s capacity to identify price-sensitive customers and high-value targets, respectively. This data-driven stratification provides a empirical foundation for implementing differentiated pricing strategies that can maximize revenue and cater to diverse customer expectations within the CRM system.
Customer distribution based on calculated experience score. While the majority report an excellent experience, the significant proportion in lower tiers identifies a key cohort for proactive service recovery and experience enhancement initiatives.
The distribution of customers across experience tiers, calculated from service interaction and usage data, provides a quantitative baseline for service quality assessment (Fig. 14). While a majority of customers fall into the ‘Excellent’ tier, a substantial cohort (approximately 1,100 customers) is classified as having ‘Satisfactory’ or sub-optimal experiences. This segmentation aligns with the predictive model’s finding that ‘customer service calls’ is a primary churn driver. The existence of this significant at-risk segment underscores the critical need for proactive intervention strategies targeted at improving the customer experience before dissatisfaction leads to attrition, thereby operationalizing the AI insights within a closed-loop CRM process.
Customer classification based on fraud risk score derived from usage pattern anomalies. The distribution validates the model’s utility in identifying a focused subset of accounts for targeted investigation, enabling efficient resource allocation for fraud prevention.
The application of anomaly detection to customer usage patterns facilitates proactive risk management alongside churn prevention. As illustrated in Fig. 15, the model classified the majority of customers as ‘Normal Risk,’ affirming the integrity of the core customer base. However, it also identified a distinct, smaller cohort flagged as ‘High Risk.’ This segmentation enables a strategic, resource-efficient approach to security, allowing for intensified monitoring and verification procedures to be focused on a high-probability subset. This demonstrates how an integrated AI-CRM system can concurrently manage multiple business objectives—in this case, mitigating revenue loss from fraudulent activities without compromising the experience for the vast majority of legitimate customers.
PCA visualization of customer segments derived from K-means clustering. The distinct clusters in the reduced principal component space represent unique customer cohorts based on service usage and behavioral patterns, enabling targeted relationship management strategies.
To complement the predictive model, customer segmentation was performed using K-means clustering on the feature set. The resulting segments, visualized via a two-dimensional Principal Component Analysis (PCA) projection in Fig. 16, reveal distinct, well-separated customer cohorts. The clear clustering in the reduced space validates that the underlying behavioral and usage data naturally separates customers into meaningful groups. These segments, ranging from potentially budget-conscious users to high-engagement premium customers, provide a strategic framework for moving beyond one-size-fits-all marketing to highly targeted, segment-specific CRM interventions, thereby personalizing the entire customer lifecycle.
Distribution of inferred customer contact preferences based on behavioral data. The results inform a data-driven communication strategy, enabling the prioritization of daytime and evening outreach while maintaining reach to a significant night-preferring segment.
Analysis of inferred customer contact preferences, derived from engagement patterns, reveals a strategic opportunity for optimizing communication workflows (Fig. 17). While a majority of customers are most receptive during daytime and evening hours, a substantial segment shows a preference for night communications. This distribution provides an empirical basis for a multi-channel communication strategy that respects customer temporal preferences. Integrating these insights allows for the automation of contact scheduling within the CRM, ensuring that retention offers and service messages are delivered at times of highest likely engagement, thereby increasing campaign efficacy and improving the overall customer experience.
Size distribution of customer segments identified for targeted campaign management. The segments are defined by key behavioral attributes, enabling prioritized and tailored retention strategies based on segment size and strategic importance.
The segmentation of the customer base for targeted campaigns, as detailed in Fig. 18, provides an empirical basis for strategic resource allocation. The segmentation analysis identifies ‘International Users’ as the largest cohort, aligning with the feature importance of the ‘International Plan,’ followed by a substantial ‘General User’ segment. The smaller, but critically important, ‘Service Needing’ and ‘Heavy Day User’ segments correspond directly to the primary churn predictors identified by the model—customer service calls and daytime usage. This structured segmentation enables a precision marketing approach, where retention resources and communication strategies can be optimally tailored to the specific characteristics and risk profiles of each group.
While the model demonstrates high overall accuracy (95.13%) and excellent precision for the churn class (0.98), the recall of 0.68 indicates that 32% of actual churners were not identified. This reflects a classic trade-off in imbalanced classification. From a business perspective, this model is calibrated for high precision, ensuring that customers flagged as ‘high-risk’ are very likely to churn, thereby optimizing the cost-efficiency of retention campaigns. However, this comes at the expense of missing some true churners, a limitation that should be considered based on the specific cost-benefit analysis of retention actions.
The high accuracy (95.13%) can be attributed to the dataset’s clear feature separability and the effectiveness of the Random Forest algorithm in capturing the underlying patterns without overfitting, as confirmed by the strong performance on the held-out test set and the 10-fold cross-validation. Furthermore, the AUC of 0.89 provides a more robust evaluation metric, confirming the model’s strong discriminatory power.
Business Implications.
-
Focus campaign efforts on International and General Users to maximize reach and impact.
-
Consider tailored messaging or offers for Service Needing Customers to improve satisfaction.
-
Explore the behavior of Heavy Day Users to understand their needs and potential value.
-
The empirical results strongly support the research hypothesis. The high accuracy and AUC of the Random Forest model confirm that AI can reliably identify customers at risk of churning. The feature importance analysis provides actionable intelligence, revealing that efforts should be concentrated on customers with high daytime usage and those who frequently contact customer service.
-
The strategic implications for telecom CRM are profound. We propose a multi-faceted approach:
-
(1) Proactive Retention Campaigns: Deploy personalized retention campaigns targeting high-risk segments identified by the model. Offers could include tailored discounts, loyalty bonus minutes, or service upgrades based on individual usage patterns.
-
(2) Enhanced Customer Service Intervention: Implement an alert system that flags customers who have made three or more service calls for proactive, high-touch support from a dedicated retention team, aiming to resolve underlying issues before they lead to churn.
-
(3) Service Quality and Plan Optimization: Utilize insights from the model to address root causes of churn, such as network quality in areas with high daytime usage or redesigning international calling plans that are associated with attrition.
-
(4) Operationalization and Integration: For maximum impact, the predictive model must be integrated directly into the company’s CRM and operational systems, enabling real-time scoring and triggering automated or semi-automated retention workflows.
Limitations and future research: This study has several limitations. First, the model was trained on a single, publicly available dataset, which may limit its generalizability to other telecom operators with different customer demographics and service structures. External validation on proprietary datasets is needed. Second, while we addressed class imbalance with SMOTE, the recall for the churn class could be further improved. Future work will explore advanced techniques like ensemble sampling and cost-sensitive learning. Third, the feature set was limited to structured data; incorporating unstructured data from customer calls and chats could enhance predictive power. Future research will also focus on real-time model deployment and A/B testing to quantitatively measure the causal impact of AI-driven interventions on churn reduction and customer lifetime value.
link